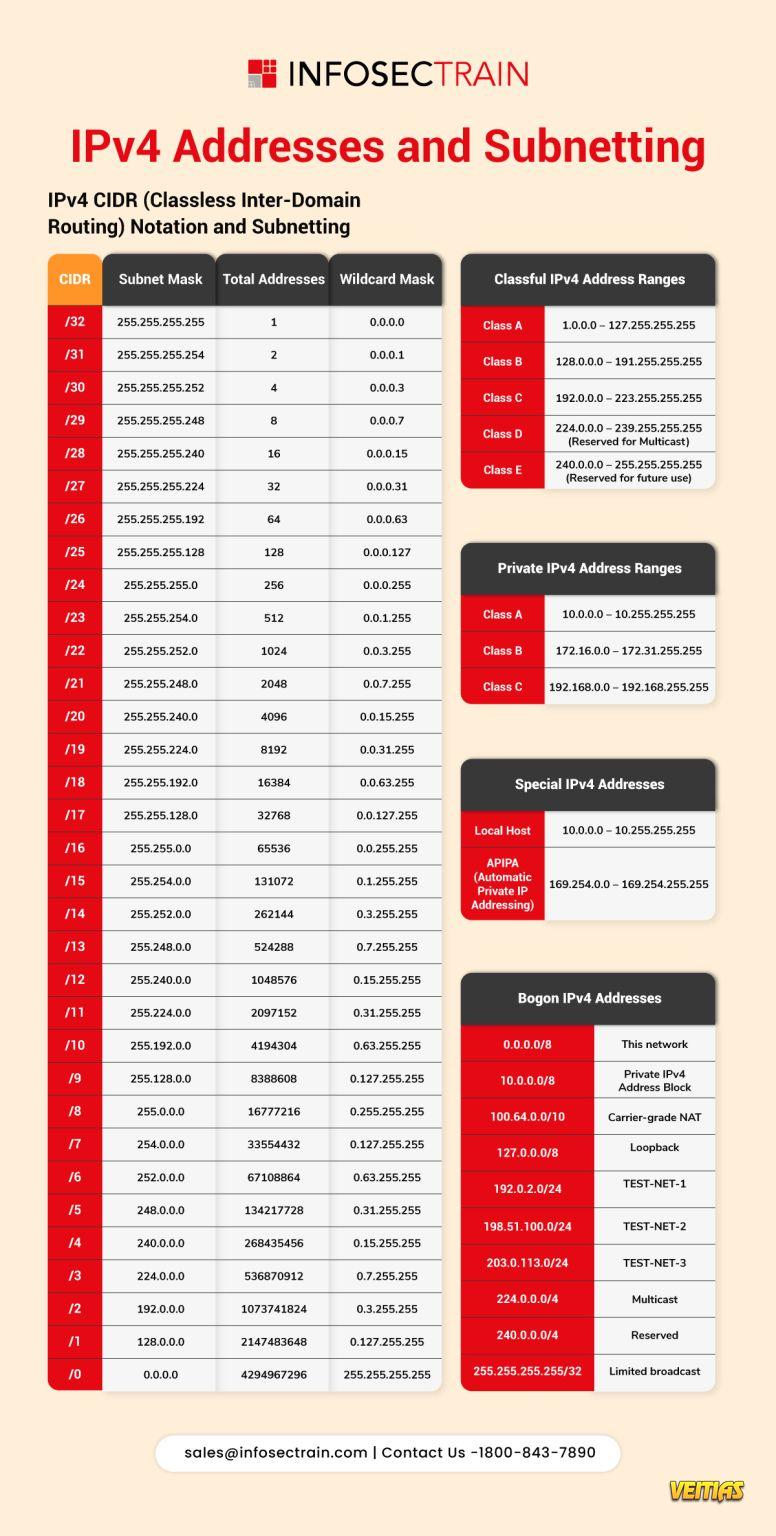
IPv4 addresses and subnetting are fundamental concepts in networking, enabling efficient communication and resource management across networks. An IPv4 address is a 32-bit numerical label assigned to devices in a network, represented in dotted decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1). These addresses are categorized into five classes (A, B, C, D, and E), with Classes A, B, and C commonly used for standard networking.
Subnetting is the process of dividing a larger network into smaller, manageable sub-networks (subnets) to improve performance, security, and address allocation efficiency. It is achieved by borrowing bits from the host portion of the IP address to create additional network segments. The subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0) determines how many bits are allocated for the network and host portions.
Subnetting is the process of dividing a larger network into smaller, manageable sub-networks (subnets) to improve performance, security, and address allocation efficiency. It is achieved by borrowing bits from the host portion of the IP address to create additional network segments. The subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0) determines how many bits are allocated for the network and host portions.
IPv4 addresses and subnetting are fundamental concepts in networking, enabling efficient communication and resource management across networks. An IPv4 address is a 32-bit numerical label assigned to devices in a network, represented in dotted decimal format (e.g., 192.168.1.1). These addresses are categorized into five classes (A, B, C, D, and E), with Classes A, B, and C commonly used for standard networking.
Subnetting is the process of dividing a larger network into smaller, manageable sub-networks (subnets) to improve performance, security, and address allocation efficiency. It is achieved by borrowing bits from the host portion of the IP address to create additional network segments. The subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0) determines how many bits are allocated for the network and host portions.
0 Comentários
0 Compartilhamentos
6614 Visualizações
0 Anterior